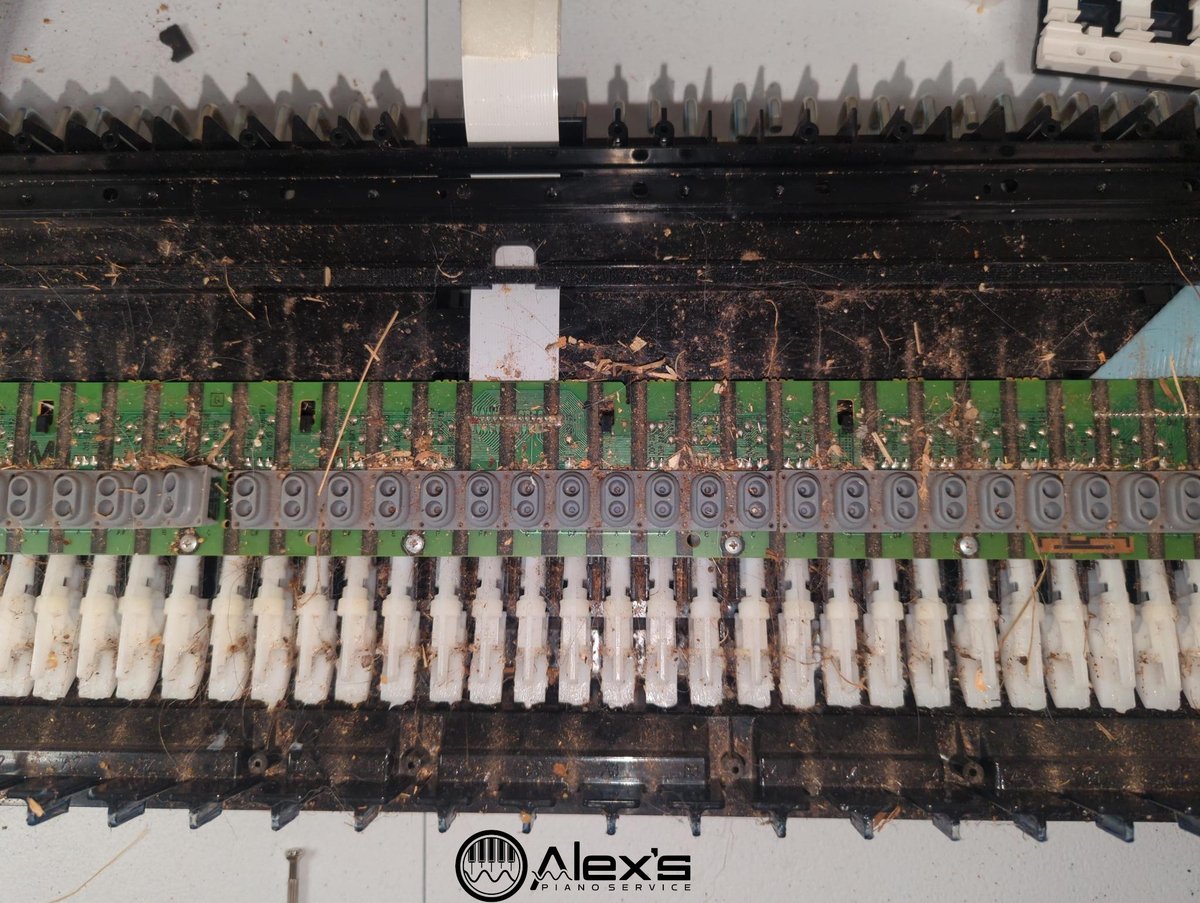
Choosing a Budget Beginner Digital Piano (Without Regrets)
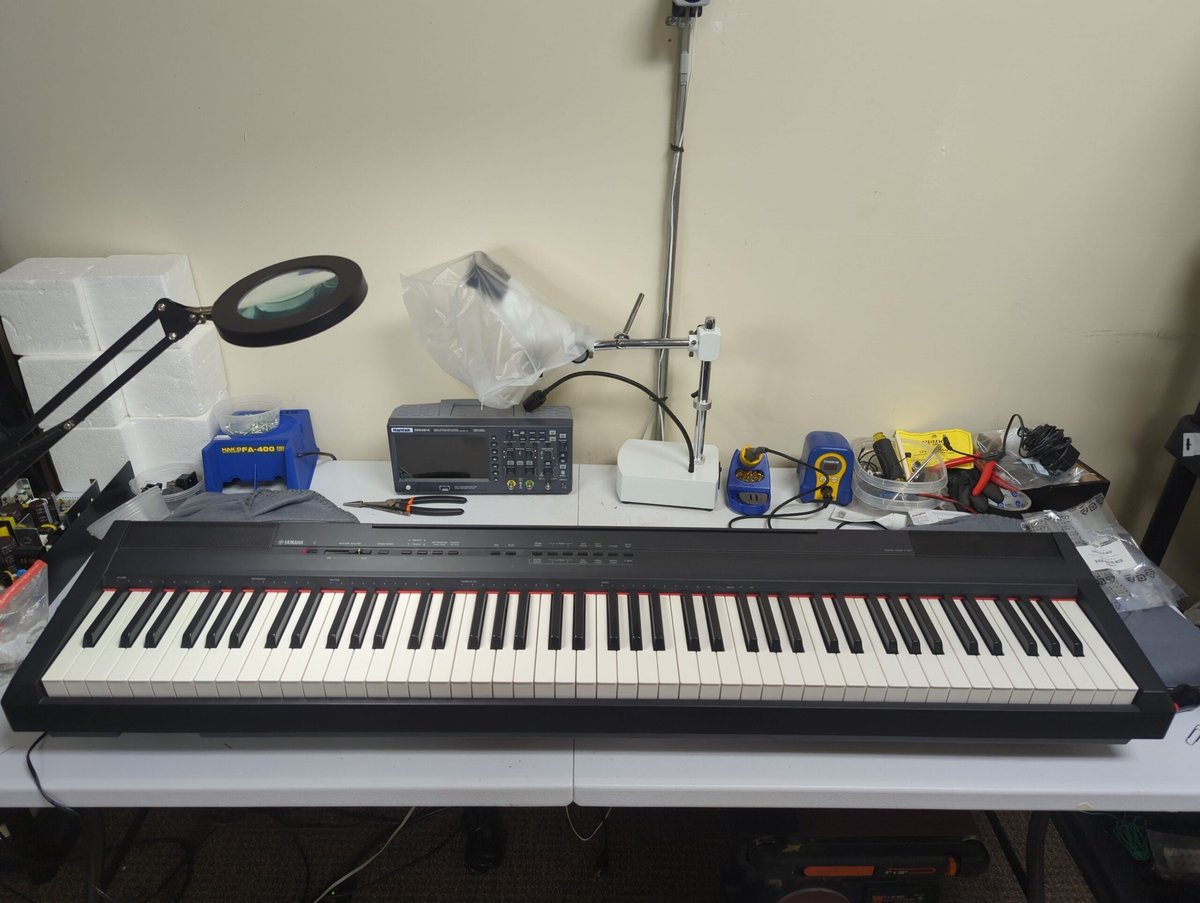
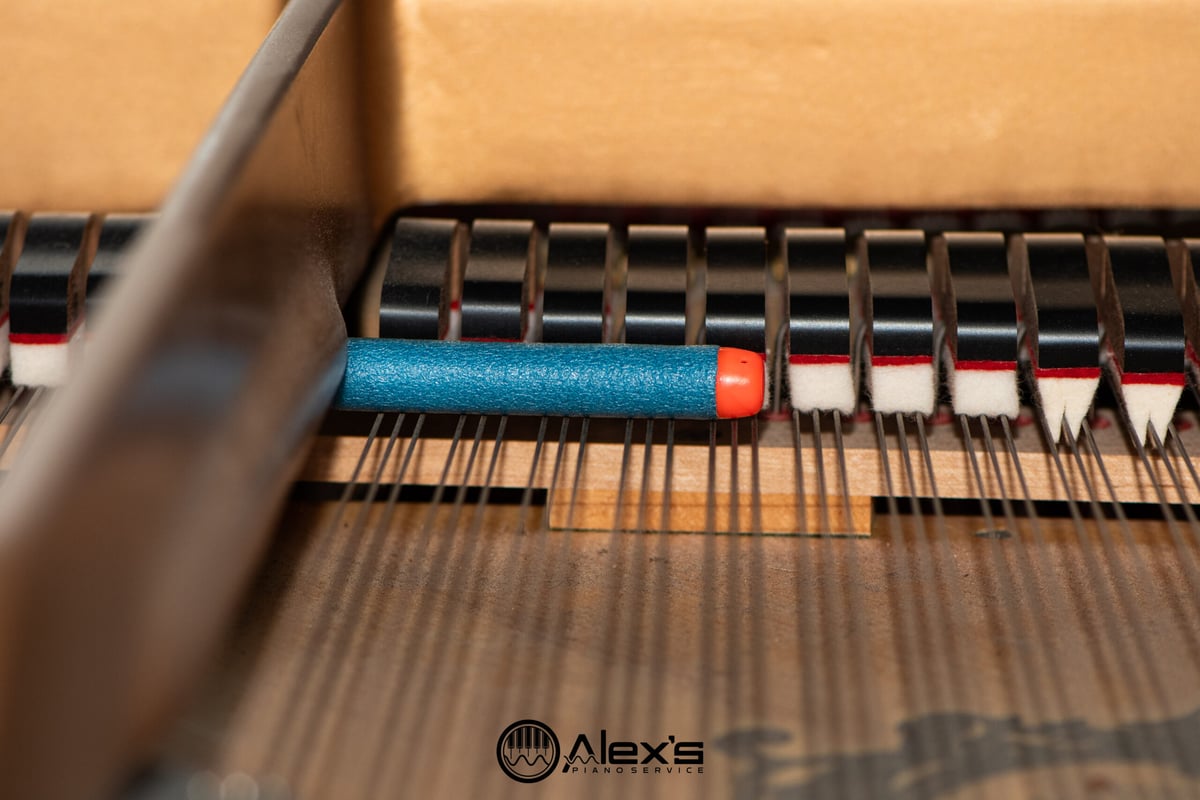
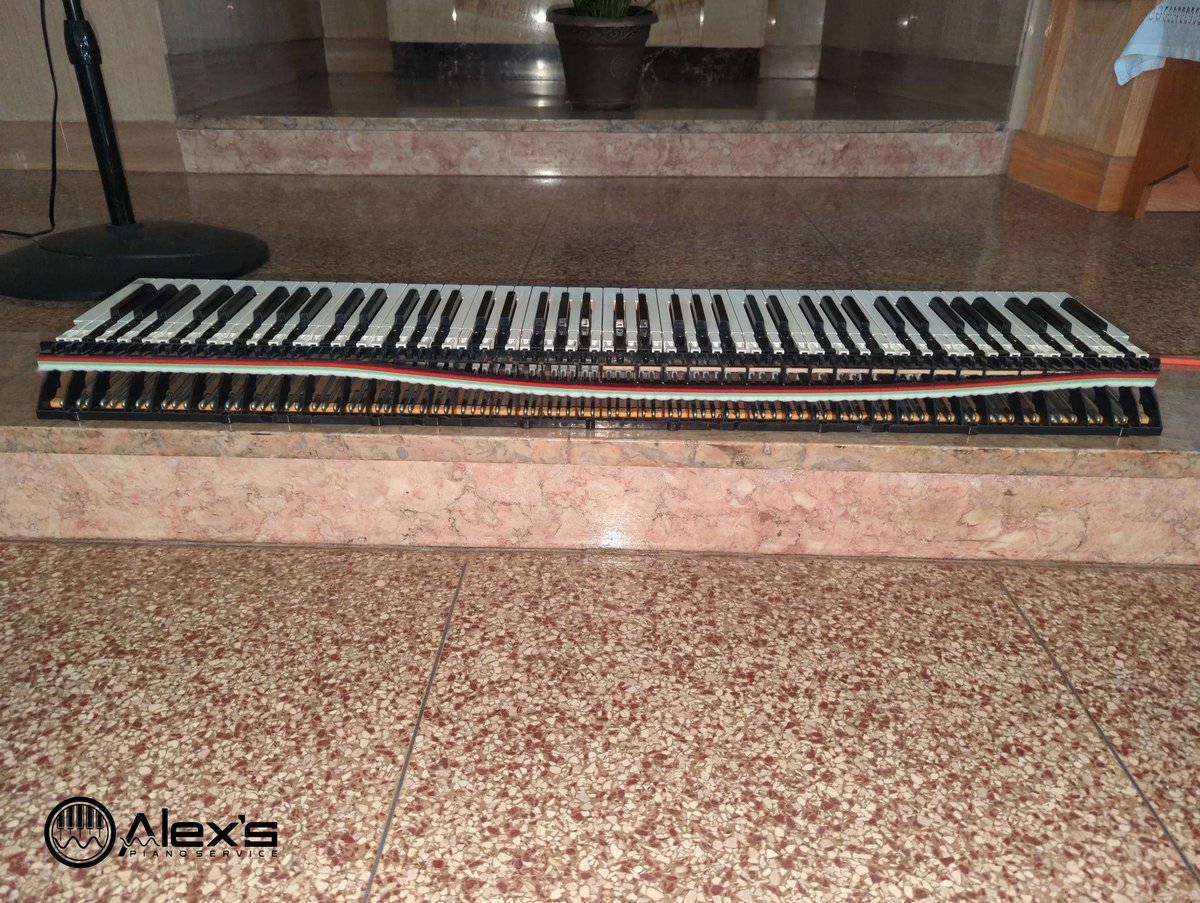
Clients regularly ask me what digital piano they should buy. Buying a “budget” digital piano is one of those decisions that feels simple, but there are many pitfalls. I’m a piano technician and an authorized service center for Yamaha, Roland, and Casio, and so I see the aftermath of these purchases all the time—good and … Read more